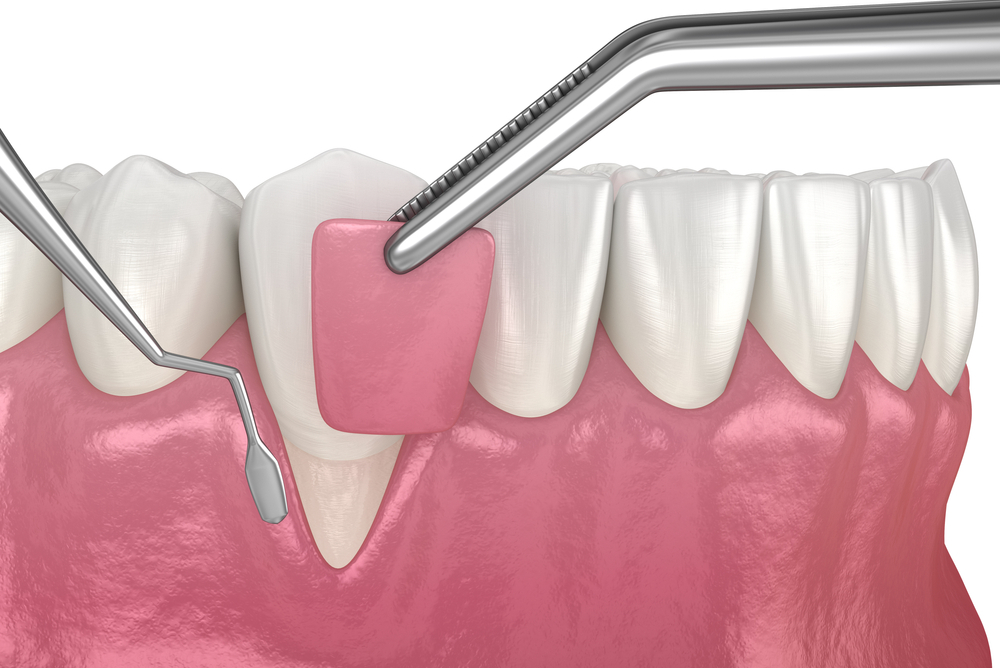
Gum grafts, also known as gingival grafts, are dental procedures aimed at repairing receding gums and restoring a healthy gum line. Receding gums can lead to tooth sensitivity, root exposure, and an unsightly appearance.
Understanding the different types of gum grafts is crucial for individuals seeking solutions to this common dental issue. In this article, we’ll delve into the various gum graft types, their procedures, and their potential benefits.
Connective Tissue Grafts
Connective tissue grafts are the most common type of gum graft performed by dental professionals. In this procedure, a small flap of skin is removed from the roof of the mouth (palate).
The connective tissue beneath the surface is then extracted and stitched to the area where gum recession has occurred. This graft helps in covering exposed roots and promoting new gum tissue growth.
The connective tissue graft is effective in addressing moderate to severe gum recession, and the palate incision is typically small, ensuring minimal discomfort for the patient.
Free Gingival Grafts
Free gingival grafts are similar to connective tissue grafts, but instead of taking tissue from the palate, the graft is directly harvested from the surface of the outer gum area. This type of graft is particularly suitable for patients with thin gums or those who require additional gum tissue to prevent further recession.
Free gingival grafts provide a thicker layer of gum tissue to protect the teeth and roots, making them an effective solution for cases where increased tissue thickness is essential.
Pedicle Grafts
Pedicle grafts involve using gum tissue from the adjacent gums near the recession site. Unlike connective tissue and free gingival grafts, pedicle grafts do not require the complete detachment of the donor tissue. Instead, a flap of tissue is partially cut and then stretched over the exposed root, covering the recession.
This type of graft is beneficial for patients who have sufficient gum tissue near the affected area and is often less invasive than other gum graft options.
Allografts and Xenografts
Allografts involve the use of donated human tissue, while xenografts utilize tissue from animals, usually cows. These grafts are often processed and sterilized before being used in the procedure.
Allografts and xenografts serve as alternatives to traditional grafts, providing a scaffold for the patient’s own cells to regenerate gum tissue. While these grafts may reduce the need for harvesting tissue from the patient, they may not be as effective in certain cases compared to autografts.
Platelet-Rich Fibrin (PRF) Grafts
Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF) grafts involve the use of the patient’s blood to create a concentrated fibrin matrix rich in platelets and growth factors. This matrix is then placed over the receding gums to stimulate natural tissue regeneration.
PRF grafts are considered a more advanced and minimally invasive option, promoting faster healing and reducing the risk of infection. This method harnesses the body’s own healing abilities to enhance the success of gum grafting in Red Deer.
Endnotes
Choosing the right type of gum graft depends on various factors, including the extent of gum recession, the thickness of existing gum tissue, and the patient’s overall oral health. Consultation with a dental professional is crucial to determining the most suitable grafting technique for individual cases.
Addressing gum recession through grafting not only improves the aesthetic appearance of the smile but also plays a crucial role in preventing further dental issues such as tooth sensitivity and decay.
With advancements in dental technology, patients now have a range of options to choose from, ensuring a tailored approach to their specific needs. If you’re experiencing a gum recession, don’t hesitate to reach out to your dentist near you to discuss the most suitable gum grafting option for you. Remember, a healthy gum line is a key component of overall oral well-being.